Trojan:W32/Rabbad
Summary
This crypto-ransomware first came to public notice on 24 October 2017 following reports that it had infected organizations in Ukraine and Russia.
Proactive protection was provided by F-Secure's DeepGuard behavioral analysis engine before this threat was publicly disclosed. Multiple signature detections were also subsequently released to provide additional, specific coverage.
Removal
F-Secure detects this ransomware with multiple behavioral and signature detections. Once detected, the F-Secure security product will automatically remove the file.
Further action
Once ransomware has successfully encrypted files on a machine, the encryption may be sufficient to make it very difficult to decrypt the files without the decryption key. In such circumstances, the recommended course of action is to report the crime to the relevant authorities and restore the affected data from a backup.
A False Positive is when a file is incorrectly detected as harmful, usually because its code or behavior resembles known harmful programs. A False Positive will usually be fixed in a subsequent database update without any action needed on your part. If you wish, you may also:
-
Check for the latest database updates
First check if your F-Secure security program is using the latest updates, then try scanning the file again.
-
Submit a sample
After checking, if you still believe the file is incorrectly detected, you can submit a sample of it for re-analysis.
NOTE If the file was moved to quarantine, you need to collect the file from quarantine before you can submit it.
-
Exclude a file from further scanning
If you are certain that the file is safe and want to continue using it, you can exclude it from further scanning by the F-Secure security product.
Note You need administrative rights to change the settings.
Technical Details
Bad Rabbit first came to public notice on 24 October 2017, as multiple security firms reported their discovery of a new ransomware family affecting a number of organizations, mainly in Russia and Ukraine.
According to reports, at least three media companies have been affected by the ransomware, as well as as transportation services.
For more information about the incident:
- BBC: 'Bad Rabbit' ransomware strikes Ukraine and Russia
- ESET: Kiev metro hit with a new variant of the infamous Diskcoder ransomware
- Motherboard: New Ransomware 'Bad Rabbit' Spreading Quickly Through Russia and Ukraine
Infection
From our analysis, the initial infection vector for the Bad Rabbit ransomware is via compromised websites that host an injected malicious script. The script redirects users to a secondary site where the actual ransomware file is downloaded. The actual file itself may be disguised as an Adobe Flash Player update.
Bad Rabbit also includes functionality to spread through a network, as it is able to check for accessible SMB shares using hardcoded usernames and passwords:
Usernames
- Administrator
- Admin
- Guest
- User
- User1
- user-1
- Test
- root
- buh
- boss
- ftp
- rdp
- rdpuser
- rdpadmin
- manager
- support
- work
- other user
- operator
- backup
- asus
- ftpuser
- ftpadmin
- nas
- nasuser
- nasadmin
- superuser
- netguest
- alex
Passwords
- Admin
- Admin123
- adminTest
- admin123Test123
- Administrator
- administrator
- Administrator123
- administrator123
- Guest
- guest
- Guest123
- guest123
- User123
- user123
- test123
- 123321
- 111111
- 55555
- 77777
- 777
- 123
- 321
- 1234
- 12345
- 123456
- 1234567
- 12345678
- 123456789
- 1234567890
- qwe
- qwe123
- qwe321
- qwer
- qwert
- qwerty
- qwerty123
- zxc
- zxc123
- zxc321
- zxcv
- uiop
- User
- user
- test
- root
- love
- secret
- sex
- god
- password
If any SMB shares are found with these usernames or passwords, Bad Rabbit then checks for open RPC pipes. If any are found, it then uses the Eternal Romance exploit to spread within the network.
The use of the NSA-linked Eternal Romance exploit to spread marks a similarity between this ransomware and the Petya.F ransomware, though Bad Rabbit uses a different implementation of it. In contrast however, Bad Rabbit does not use the EternalBlue exploit, which is also used by Petya.
When the Bad Rabbit file is executed on a machine, it drops a file named 'C:\Windows\infpub.dat', a DLL that in turn drops the following files:
- C:\Windows\cscc.dat - installed as a service and renamed DCRYPT.SYS (a legitimate file name from the ReactOS)
- C:\Windows\dispci.exe - A file decrypter. A shortcut link (DECRYPT.lnk) is also added to the file on the Desktop
The infpub.dat file will also create the following Windows tasks:
- %System32%\Tasks\rhaegal
- %System32%\Tasks\drogon
- %System32%\Tasks\viserion
And registry keys:
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Schedule\TaskCache\Tree\drogon
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Schedule\TaskCache\Tree\rhaegal
- HKLM\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\services\cscc
- HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\cscc
- HKLM\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\services\cscc\ImagePath: "cscc.dat"
- HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\cscc\ImagePath: "cscc.dat"
The task names and registry keys reference the popular television series, Game of Thrones.
Encryption
Once Bad Rabbit is installed, it will encrypt files stored on the machine. The ransomware targets the following types of files:
- .3ds, .7z
- .accdb, .ai, .asm, .asp, .aspx, .avhd
- .back, .bak, .bmp, .brw
- .c, .cab, .cc, .cer, .cfg, .conf, .cpp, .crt, .cs, .ctl, .cxx
- .dbf, .der, .dib, .disk, .djvu, .doc, .docx, .dwg
- .eml
- .fdb
- .gz
- .h, .hdd, .hpp, .hxx
- .iso
- .java, .jfif, .jpe, .jpeg, .jpg, .js
- .kdbx, .key
- .mail, .mdb, .msg
- .nrg
- .odc, .odf, .odg, .odi,.odm, .odp, .ods, .odt, .ora, .ost, .ova, .ovf
- .p12, .p7b, .p7c, .pdf, .pem, .pfx, .php, .pmf, .png, .ppt,.pptx, .ps1, .pst, .pvi, .py, .pyc, .pyw
- .qcow, .qcow2
- .rar, .rb, .rtf
- .scm, .sln, .sql
- .tar, .tib, .tif, .tiff
- .vb, .vbox, .vbs, .vcb, .vdi, .vfd, .vhd, .vhdx, .vmc, .vmdk, .vmsd, .vmtm, .vmx, .vsdx, .vsv
- .work
- .xls, .xlsx, .xml, .xvd
- .zip
Bad Rabbit uses a driver from the open-source DisCryptor disk encryption software to perform the encryption. After rebooting the machine, the driver runs AES string encryption using a randomly generated key, which is then encrypted with the ransomware's hard-coded public key and then encoded to the machine's Master Boot Record (MBR) This code is intended for later use during the ransom payment process.
Bad Rabbit's encryption behavior shows similarities to the known Petya ransomware.
Unlike other ransomware, Bad Rabbit does not change the extensions of the encrypted files, making it less obvious that they have been tampered with. It does however add the string 'encrypted' to the end of the encrypted file.
Ransom demand
Once the files are encrypted, Bad Rabbit will display the following ransom demand:
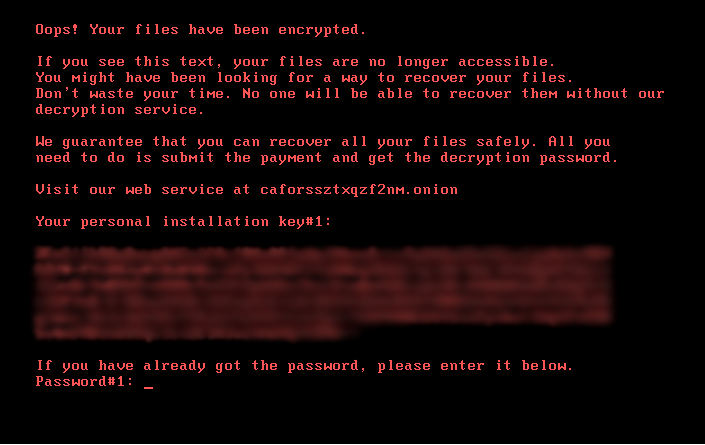
Ransom demand displayed by Bad Rabbit ransomware
Users are directed to pay the ransom at a specified payment site, which also provides the amount of the ransom to be paid.
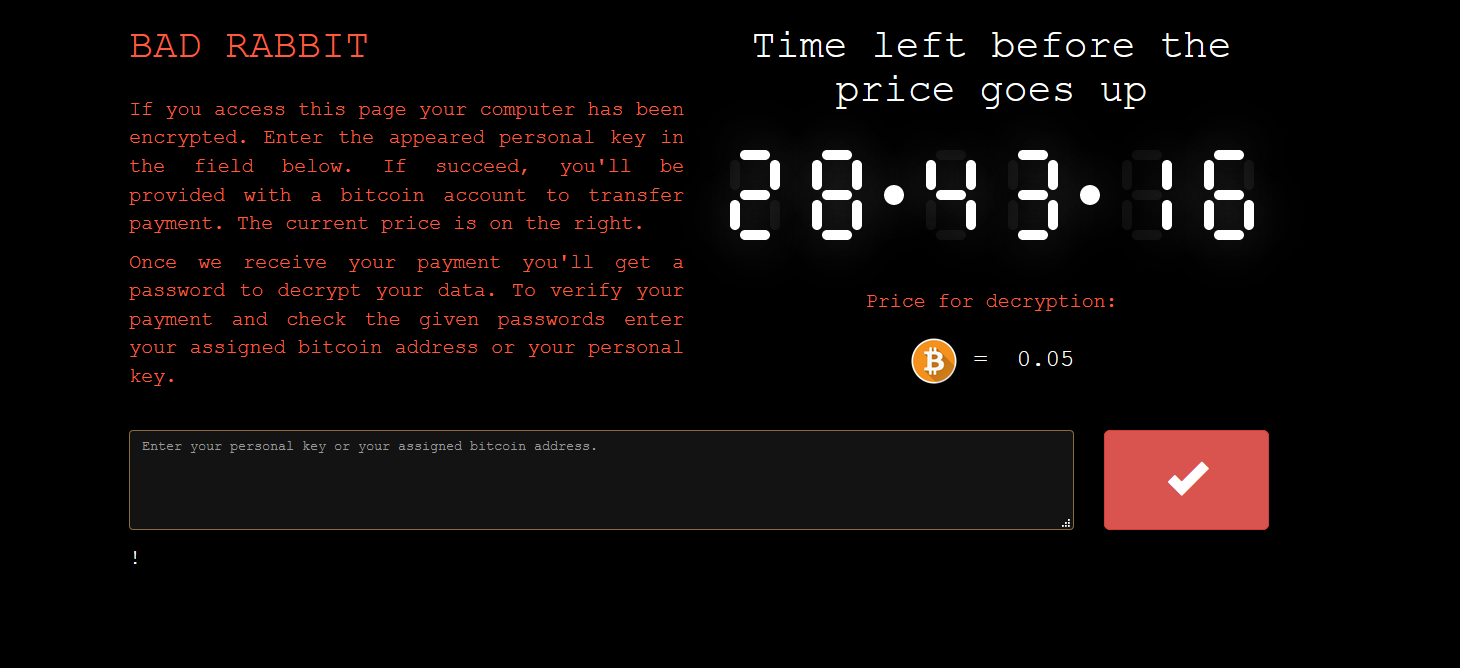
Bad Rabbit payment site