Trojan:OSX/DNSChanger
Summary
Trojan:OSX/DNSChanger are detections of installation packages, masked as fake codec installations for Mac OS X computers.
Removal
The F-Secure security product will automatically remove the file.
Restoring DNS Settings
-
Open the Apple Network Pane:
- Applications >System Preferences >Network
-
Set the correct DNS Server, or leave it blank if you
use a DHCP server.

-
To double check the DNS settings, click the
Advanced button and choose the DNS tab:
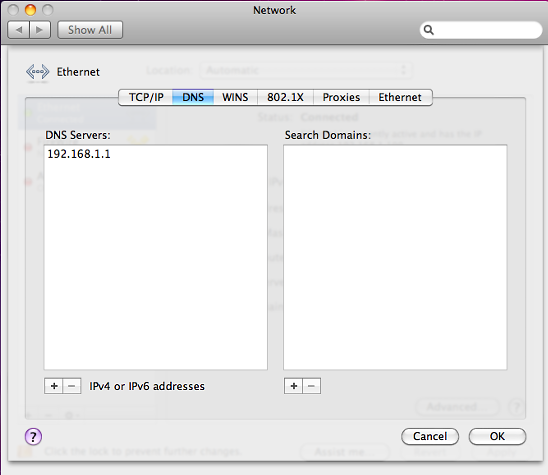
- Click the OK button, then the Apply button.
A False Positive is when a file is incorrectly detected as harmful, usually because its code or behavior resembles known harmful programs. A False Positive will usually be fixed in a subsequent database update without any action needed on your part. If you wish, you may also:
-
Check for the latest database updates
First check if your F-Secure security program is using the latest updates, then try scanning the file again.
-
Submit a sample
After checking, if you still believe the file is incorrectly detected, you can submit a sample of it for re-analysis.
Note: If the file was moved to quarantine, you need to collect the file from quarantine before you can submit it.
-
Exclude a file from further scanning
If you are certain that the file is safe and want to continue using it, you can exclude it from further scanning by the F-Secure security product.
Note: You need administrative rights to change the settings.
Technical Details
These trojans start in the package install scripts.
Installation
Social engineering techniques are used to persuade the user into downloading and running this trojan. Websites hosting video (often illicit) claim that the video cannot be viewed without installing a new codec. The user is prompted to install the "needed" codec.
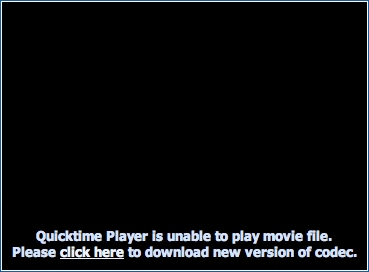
The user then downloads:

Installing the fake codec:
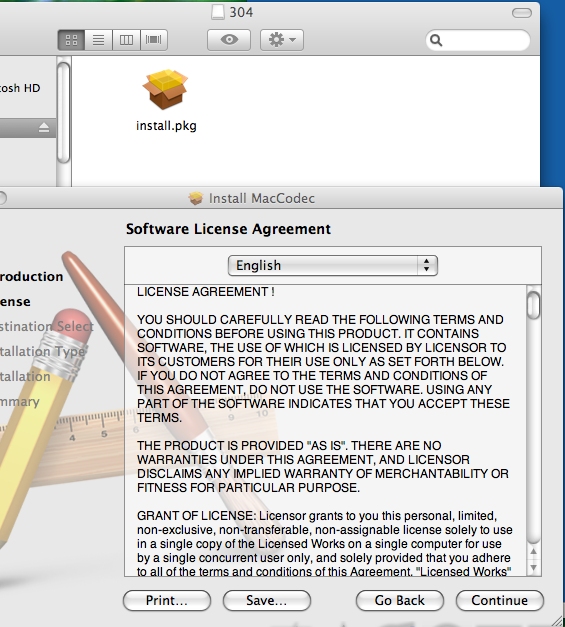
Once the fake codec is installed, the video will play so as not to raise suspicion. During the installation, the local machine's DNS settings are adjusted to point towards a malicious server.
Changes the DNS Server
The trojan changes the OS X network settings to use a different DNS server. DNS Settings are made with a tool called scutil.
The DNS Server Addresses vary. For example, Trojan:OSX/DNSChanger.A directs traffic to servers located in Ukraine.
Reports Back
After installation, the script sends back an HTTP message with information that it successfully infected the system. The message contains the operating system version and the host name.
Prevents Disinfection
The install script adds a crontab (a configuration file that specifies shell commands to run periodically on a given schedule) to a script to verify the malicious DNS servers remain unchanged. The script is stored in /Library/Internet Plug-Ins and is named plugins.settings.
The trojan infects both 10.4 and 10.5 versions of Mac OS X.
)
Protect your devices from malware with F‑Secure Total
Protecting your devices from malicious software is essential for maintaining online security. F‑Secure Total makes this easy, helping you to secure your devices in a brilliantly simple way.
- Award-winning antivirus and malware protection
- Online browsing, banking, and shopping protection
- 24/7 online identity and data breach monitoring
- Unlimited VPN service to safeguard your privacy
- Password manager with private data protection
More Support
Community
Ask questions in our Community .
User Guides
Check the user guide for instructions.
Submit a Sample
Submit a file or URL for analysis.