Net-Worm:W32/Sasser
Summary
Net-Worm:W32/Sasser refers to a small family of worms that spread to new hosts over the Internet by targeting the known MS04-011 (LSASS) vulnerability, which is caused by a buffer overrun in the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service.
Removal
Allow F-Secure Anti-Virus to disinfect the relevant files.
CAUTION Manual disinfection is a risky process; it is recommended only for advanced users.
To manually disinfect an infected system, first apply the Microsoft patch MS04-011, then use Task Manager to kill the "avserve.exe" process, then delete the file AVSERVE.EXE from your Windows directory and reboot.
For step-by-step instructions, see Microsoft's site:
https://www.microsoft.com/security/incident/sasser.asp#steps
A False Positive is when a file is incorrectly detected as harmful, usually because its code or behavior resembles known harmful programs. A False Positive will usually be fixed in a subsequent database update without any action needed on your part. If you wish, you may also:
-
Check for the latest database updates
First check if your F-Secure security program is using the latest updates, then try scanning the file again.
-
Submit a sample
After checking, if you still believe the file is incorrectly detected, you can submit a sample of it for re-analysis.
Note: If the file was moved to quarantine, you need to collect the file from quarantine before you can submit it.
-
Exclude a file from further scanning
If you are certain that the file is safe and want to continue using it, you can exclude it from further scanning by the F-Secure security product.
Note: You need administrative rights to change the settings.
Technical Details
Sasser will affect all machines that are:
- Running Windows XP or Windows 2000
- Haven't been patched against the known MS04-011 (LSASS) vulnerability
- Are connected to the Internet without a firewall
This vulnerability has been addressed and patched. For more information, please refer to the Microsoft Bulletin (http://www.microsoft.com/technet/security/bulletin/MS04-011.mspx) for more details.
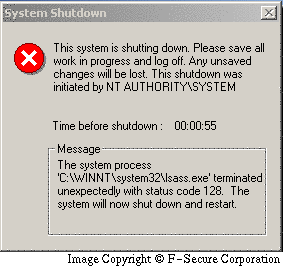
Sign of infection is the existence of a file named 'C:\win.log' and frequent crashes of 'LSASS.EXE'. Sasser generates traffic on TCP ports 445, 5554 and 9996.
Sasser was written in Visual C++; the first variant, Sasser.A, spreads in a single executable which is packed and protected with several envelopes. A later variant, Sasser.B, using the filename AVSERVE2.EX.
Infection
When the worm enters the system it creates a copy of itself in the Windows Directory as 'avserve.exe'. This copy is added to the Registry as:
- [SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run] "avserve.exe" = "%WinDir%\avserve.exe"
To ensure that only one copy of the worm is running it creates a mutex named 'Jobaka3l'.
Network Propagation
Sasser exploits the the MS04-011 (LSASS) vulnerability to gain access the remote systems. The worm starts 128 scanning threads that try to find vulnerable systems on random IP addresses. Computers are probed on port 445 which is the default port for Windows SMB communication on NT-based systems.
The probing might crash unpatched computers.
Under Windows 2000, users can see a Windows error message like this:
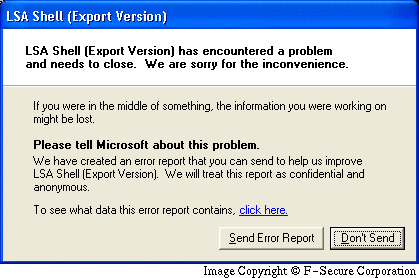
Under Windows XP, users can see a Windows error message saying:
When attacking the worm first determines the version of the remote operating system then uses the appropriate parameters to attack the host.
Different parameters are used for
- - Windows XP (universal exploit)
- - Windows 2000 (universal exploit)
- - Windows 2000 Advanced Server (SP4 exploit)
Other operating systems, such as Windows Me and NT are not infected by this worm.
If the attack is successful a shell is started on port 9996. Through the shell port Sasser instructs the remote computer to download and execute the worm from the attacker computer using FTP. The FTP server listens on port 5554 on all infected computers with the purpose of serving out the worm for other hosts that are being infected. Transactions through the FTP server are logged to 'C:\win.log'.
Summary of TCP ports used by the worm:
- 445/TCP: The worm attacks through this port
- 5554/TCP: FTP server on infected systems
- 9996/TCP: Remote shell opened by the exploit on the vulnerable hosts