Backdoor:W32/Padodor.W
Summary
A remote administration tool (RAT) that bypasses the security features of a program, computer or network to give unauthorized access or control to its user.
Removal
Based on the settings of your F-Secure security product, it will either move the file to the quarantine where it cannot spread or cause harm, or remove it.
A False Positive is when a file is incorrectly detected as harmful, usually because its code or behavior resembles known harmful programs. A False Positive will usually be fixed in a subsequent database update without any action needed on your part. If you wish, you may also:
-
Check for the latest database updates
First check if your F-Secure security program is using the latest updates, then try scanning the file again.
-
Submit a sample
After checking, if you still believe the file is incorrectly detected, you can submit a sample of it for re-analysis.
Note: If the file was moved to quarantine, you need to collect the file from quarantine before you can submit it.
-
Exclude a file from further scanning
If you are certain that the file is safe and want to continue using it, you can exclude it from further scanning by the F-Secure security product.
Note: You need administrative rights to change the settings.
Technical Details
Backdoor:W32/Padodor.W variant was found early on June 25th, 2004 as the result of an investigation into Trojan:W32/Scob.The original Padodor backdoor source code was used to create this variant, but the backdoor functionality was removed to effectively create a trojan, which steals personal information including credit card numbers, logins and passwords, and other sensitive data.
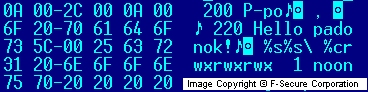
The trojan's file is a PE executable 51712 bytes long. The trojan's file is encrypted and the decryption routine is polymorphic. Every time the trojan installs itself, it changes its decryptor, so its file will look different after every installation.The original backdoor code contains rootkit functionality, but this variant uses it only to hide its processes, not its files. It should be noted that the files are still visible if viewed from Command shell (CMD.EXE). Based on available evidence, the original Padodor code was suspected to be a creation of a Russian hacker group called HangUp Team. Until the G variant was released, their copyright was in the backdoor files:

Subsequently, the copyright string was removed, but the project name "padonok" (an incorrectly spelled Russian word "podonok" that means "scum") remained:
Installation
When the trojan's file is run, it copies its file to Windows System directory with a random name that can contain '32' in the end (e.g., 'amackg32.exe').It then extracts and writes a small DLL file to Windows System folder, which also has a randomly generated name that can contain '32' in the end, (e.g.,'bnldnl32.dll'). The DLL file is a starter for the trojan's executable file and contains the name of the dropped trojan file, as it is inserted there before extaction.
The trojan creates the registry key:
- [HKCR\CLSID\{79FEACFF-FFCE-815E-A900-316290B5B738}\InProcServer32] @ = "%WinSysDir%\.dll" "ThreadingModel" = "Apartment"
where %WinSysDir% represents the name of Windows System folder and represends randomly generated file name. As a result, the DLL gets loaded every time Windows starts and it activates the trojan's file.
It also creates the following Registry key value:
- [HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ShellServiceObjectDelayLoad] "Web Event Logger" = "{79FEACFF-FFCE-815E-A900-316290B5B738}"
The trojan creates a mutex named 'KingKarton_10' and checks it at startup to avoid loading several copies of itself to memory.
As a record, the trojan creates the 'surf.dat' file in the Windows System folder and writes the computer name and user name there every time it activates.
Activity
When the trojan is active, one of its threads is constantly looking for the following text strings in Microsoft Internet Explorer windows:
- .paypal.com
- signin.ebay.
- .earthlink.
- .juno.com
- my.juno.com/s/
- webmail.juno.com
- .yahoo.com
and
- Sign In
- Log In
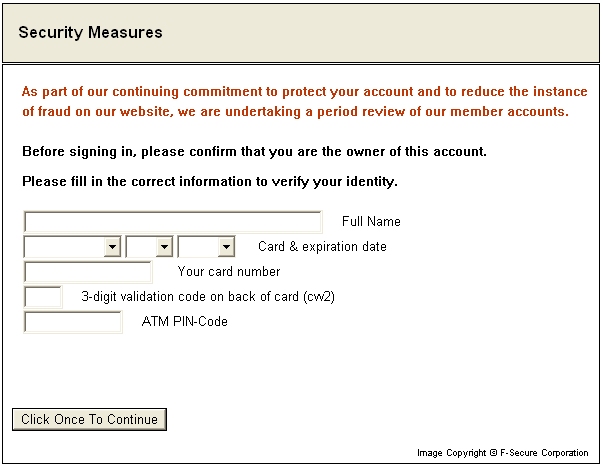
If such text strings are found, the trojan tracks the login and password entered by the user and saves it to a file called DNKK.DLL located in Windows System folder. The trojan can also display a fake webform and ask a user to select his/her credit card type, input his/her full name, credit card number, expiration date, CVV2 code and ATM PIN. The collected data is stored in a file called KK32.DLL file located in Windows System folder. Here's a screenshot of the fake form displayed by the trojan:
The trojan creates a thread that periodically creates or changes the following Registry keys:
- [HKCU\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\Zones\ [zone] ] "1601" =
- [HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings] "GlobalUserOffline" =
- [HKU\.DEFAULT\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\BrowseNewProcess] "BrowseNewProcess" = "yes"
The thread creates an HTML file where it copies stolen data, opens it with Internet Explorer and the data gets submitted to one following websites (selected randomly) using a small script:
- http://crutop.nu/index.php
- http://crutop.ru/index.php
- http://mazafaka.ru/index.php
- http://color-bank.ru/index.php
- http://asechka.ru/index.php
- http://trojan.ru/index.php
- http://fuck.ru/index.php
- http://goldensand.ru/index.php
- http://filesearch.ru/index.php
- http://devx.nm.ru/index.php
- http://ros-neftbank.ru/index.php
- http://lovingod.host.sk/index.php
- http://www.redline.ru/index.php
- http://cvv.ru/index.php
- http://hackers.lv/index.php
- http://fethard.biz/index.php
After submitting the data, the trojan checks for feedback from the site and if it is a string equal to 'X-okRecv11', the trojan deletes the HTML file and terminates Internet Explorer process. The trojan creates another thread that periodically accesses the following webpages:
- http://ldark.nm.ru/index.htm
- http://gaz-prom.ru/index.htm
- http://promo.ru/index.htm
- http://potleaf.chat.ru/index.htm
- http://kadet.ru/index.htm
- http://cvv.ru/index.htm
- http://crutop.nu/index.htm
- http://crutop.ru/index.htm
- http://mazafaka.ru/index.htm
- http://xware.cjb.net/index.htm
- http://konfiskat.org/index.htm
- http://parex-bank.ru/index.htm
- http://kidos-bank.ru/index.htm
- http://kavkaz.ru/index.htm
- http://ldark.nm.ru/index.htm
- http://fethard.biz/index.htm
Before accessing the above mentioned websites the trojan creates an HTML file with a special script. If the index.htm page on these sites contain 'X-okRecv11' string the trojan terminates Internet Explorer and deletes the created HTML file. Otherwise the trojan browses Internet cache files and appends the last used HTML file to the KK32.VXD file located in Windows System folder.
It should be noted that during the operation described above the trojan creates a new desktop called 'blind_user' on an infected computer that a user can not see and then opens Internet Explorer there.