Email-Worm:W32/Bagle.AT
Summary
This type of worm is embedded in an email attachment, and spreads using the infected computer's emailing networks.
Removal
Based on the settings of your F-Secure security product, it will either move the file to the quarantine where it cannot spread or cause harm, or remove it.
A False Positive is when a file is incorrectly detected as harmful, usually because its code or behavior resembles known harmful programs. A False Positive will usually be fixed in a subsequent database update without any action needed on your part. If you wish, you may also:
-
Check for the latest database updates
First check if your F-Secure security program is using the latest updates, then try scanning the file again.
-
Submit a sample
After checking, if you still believe the file is incorrectly detected, you can submit a sample of it for re-analysis.
Note: If the file was moved to quarantine, you need to collect the file from quarantine before you can submit it.
-
Exclude a file from further scanning
If you are certain that the file is safe and want to continue using it, you can exclude it from further scanning by the F-Secure security product.
Note: You need administrative rights to change the settings.
Technical Details
Email-Worm:W32/Bagle.AT spreads via email file attachments and through Peer-to-Peer (P2P) networks, as well as through a prepended Windows Control Panel Applet (CPL) stub.
This worm is programmed to cease its activity on Apr 25th, 2006.
Infection
Bagle.AT arrives a file attachment to an email message, which has varying subject lines and body texts. The attachment is an executable file with one the following extensions: .EXE, .SCR, .COM and .CPL. The worm uses several different icons for the attachments it sends, such as these:
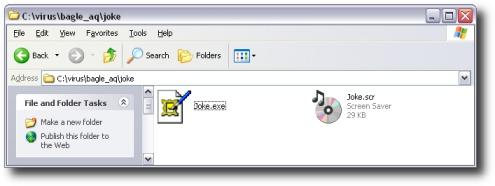
When the worm's file is run, it copies itself as wingo.exe to Windows System folder and creates a startup key for this file in the Registry:
- [HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run] "wingo" = "%SystemDir%\ wingo.exe"
%SystemDir% represents the Windows System folder name, for example C:\Windows\System32 on Windows XP systems.
If system date is Apr 25th, 2006 the worm uninstalls itself from the infected system by deleting its startup key in the Registry and terminating its own process.
The worm creates 2 more files in Windows System folder:
- wingo.exeopen
- wingo.exeopenopen
These files are used when the worm spreads itself in emails.
Propagation (email)
To find new victims, Bagle.AT scans the hard drive to collect email addresses. Files with the following extensions are checked:
- .wab
- .txt
- .msg
- .htm
- .shtm
- .stm
- .xml
- .dbx
- .mbx
- .mdx
- .eml
- .nch
- .mmf
- .ods
- .cfg
- .asp
- .php
- .pl
- .wsh
- .adb
- .tbb
- .sht
- .xls
- .oft
- .uin
- .cgi
- .mht
- .dhtm
- .jsp
The worm ignores email addresses that contain any of the following strings:
- @hotmail
- @msn
- @microsoft
- rating@
- f-secur
- news
- update
- anyone@
- bugs@
- contract@
- feste
- gold-certs@
- help@
- info@
- nobody@
- noone@
- kasp
- admin
- icrosoft
- support
- ntivi
- unix
- bsd
- linux
- listserv
- certific
- sopho
- @foo
- @iana
- free-av
- @messagelab
- winzip
- winrar
- samples
- abuse
- panda
- cafee
- spam
- pgp
- @avp.
- noreply
- local
- root@
- postmaster@
Bagle.AT spreads itself in emails with randomly-chosen subject lines, mail bodies and attachment names. Bagle.AT uses the following text strings as subjects for infected emails that it sends:
- Re:
- Re: Hello
- Re: Thank you!
- Re: Thanks :)
- Re: Hi
Message bodies are randomly chosen from a predefined list:
- :)
- :))
Attachment names can be one of the following names with EXE, SCR, COM, and CPL extension:
- Price
- price
- Joke
When the worm copies itself in shared folder or sends itself as an email attachment, it changes the icon file of the executable. The icon is picked randomly from the infected computer's hard drive.
Propagation (CPL)
When spreading as a Windows Control Panel Applet file, the worm prepends a small binary dropper to its executable file. When the CPL file is activated, it copies itself as cjector.exe file to Windows folder and then drops the worm's file into Windows System folder.
Propagation (P2P)
Bagle.AT is capable of spreading to shared folders of Peer-to-Peer clients. It scans all available drives and if it finds a folder name that contains 'shar' substring, the worm copies itself there with the following names:
- Microsoft Office 2003 Crack, Working!.exe
- Microsoft Windows XP, WinXP Crack, working Keygen.exe
- Microsoft Office XP working Crack, Keygen.exe
- Porno, sex, oral, anal cool, awesome!!.exe
- Porno Screensaver.scr
- Serials.txt.exe
- KAV 5.0
- Kaspersky Antivirus 5.0
- Porno pics arhive, xxx.exe
- Windows Sourcecode update.doc.exe
- Ahead Nero 7.exe
- Windown Longhorn Beta Leak.exe
- Opera 8 New!.exe
- XXX hardcore images.exe
- WinAmp 6 New!.exe
- WinAmp 5 Pro Keygen Crack Update.exe
- Adobe Photoshop 9 full.exe
- Matrix 3 Revolution English Subtitles.exe
- ACDSee 9.exe
Activity
The worm has a backdoor that listens on port 81. The backdoor code is encrypted with a password. The worm author who knows the password can connect to the computer and execute arbitrary programs. Infected computers are reported to the worm's author by accessing several predefined URLs.
The worm also tries to download and execute a file from list of predefined URLs. The downloaded file is saved on disk under the following name:
- %SystemDir%\re_file.exe
At the time of this writing, some of the URLs are functional. The file is a downloader that tries to access another list of predefined URLs.
Finally, Bagle.AT terminates processes of security and antivirus software as well as some other applications. Processes of the following applications are terminated:
- mcagent.exe
- mcvsshld.exe
- mcshield.exe
- mcvsescn.exe
- mcvsrte.exe
- DefWatch.exe
- Rtvscan.exe
- ccEvtMgr.exe
- NISUM.EXE
- ccPxySvc.exe
- navapsvc.exe
- NPROTECT.EXE
- nopdb.exe
- ccApp.exe
- Avsynmgr.exe
- VsStat.exe
- Vshwin32.exe
- alogserv.exe
- RuLaunch.exe
- Avconsol.exe
- PavFires.exe
- FIREWALL.EXE
- ATUPDATER.EXE
- LUALL.EXE
- DRWEBUPW.EXE
- AUTODOWN.EXE
- NUPGRADE.EXE
- OUTPOST.EXE
- ICSSUPPNT.EXE
- ICSUPP95.EXE
- ESCANH95.EXE
- AVXQUAR.EXE
- ESCANHNT.EXE
- ATUPDATER.EXE
- AUPDATE.EXE
- AUTOTRACE.EXE
- AUTOUPDATE.EXE
- AVXQUAR.EXE
- AVWUPD32.EXE
- AVPUPD.EXE
- CFIAUDIT.EXE
- UPDATE.EXE
- NUPGRADE.EXE
- MCUPDATE.EXE
- pavsrv50.exe
- AVENGINE.EXE
- APVXDWIN.EXE
- pavProxy.exe
- navapw32.exe
- navapsvc.exe
- ccProxy.exe
- navapsvc.exe
- NPROTECT.EXE
- SAVScan.exe
- SNDSrvc.exe
- symlcsvc.exe
- LUCOMS~1.EXE
- blackd.exe
- bawindo.exe
- FrameworkService.exe
- VsTskMgr.exe
- SHSTAT.EXE
- UpdaterUI.exe
Uninstalling the NetSky Worm
To disable the NetSky worm, Bagle.AT removes a number of registry values from under
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- My AV
- Zone Labs Client Ex
- 9XHtProtect
- Antivirus
- Special Firewall Service
- service
- Tiny AV
- ICQNet
- HtProtect
- NetDy
- Jammer2nd
- FirewallSvr
- MsInfo
- SysMonXP
- EasyAV
- PandaAVEngine
- Norton Antivirus AV
- KasperskyAVEng
- SkynetsRevenge
- ICQ Net
Additionally the worm creates several MUTEXes with names that are used by NetSky worm, so that certain versions of NetSky will not infect a system where the Bagle.AT worm is active.